Unique Pump System, Kailash Industrial Complex, Vikhroli West
A gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump that transfers fluid by trapping a fixed volume between the teeth of rotating gears and the pump casing, then carrying that fluid from the inlet to the outlet. Because each revolution moves a precise, consistent volume, flow rate is directly proportional to rotational speed — and largely independent of system pressure.
In simple terms: a gear pump does not push fluid with centrifugal force — it mechanically carries it. This fundamental difference makes gear pumps the preferred choice for viscous fluids, metering applications, and hydraulic systems where accuracy and consistency matter most.
The gear pump concept dates to around 1604, when astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler first described the mechanism. Today, gear pumps are one of the most widely used pump types in industrial and hydraulic fluid handling worldwide.
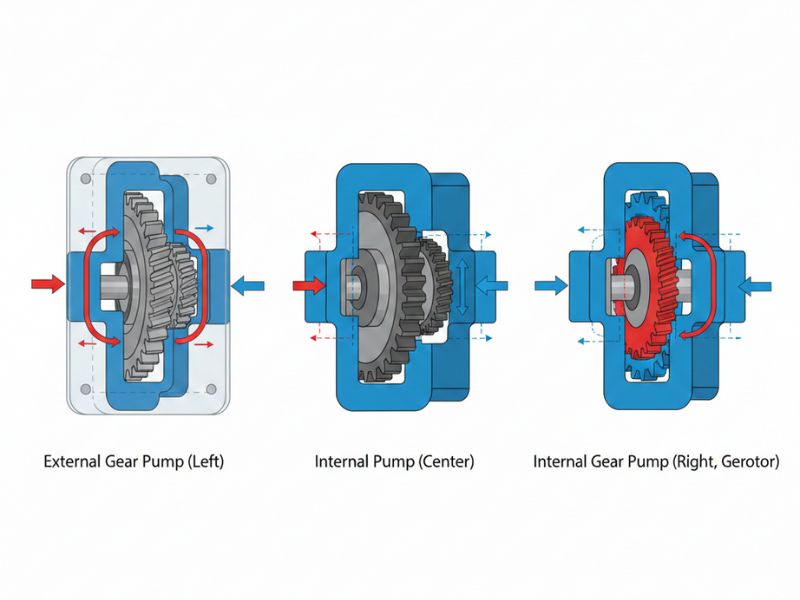
There are two primary gear pump designs used in industrial applications, each suited to different fluid types and pressure requirements.
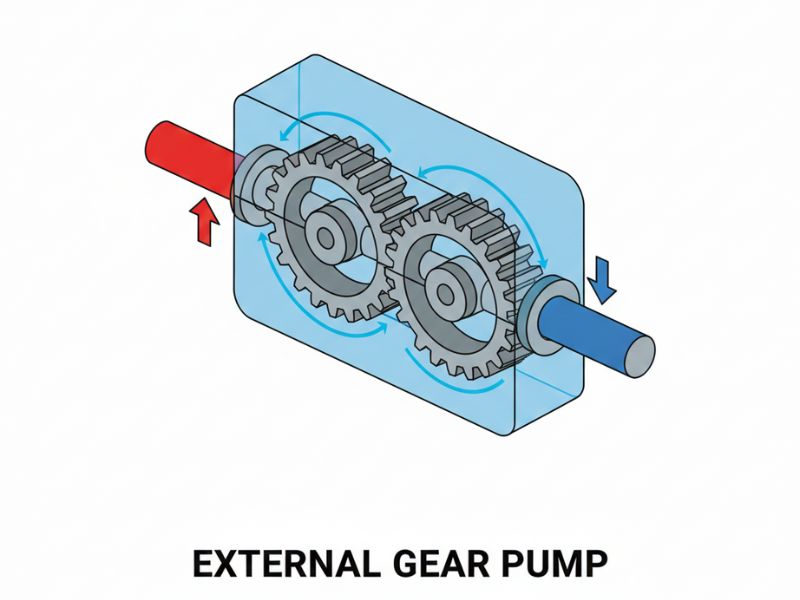
An external gear pump uses two identical external gears rotating in opposite directions inside a casing. One gear is driven by a motor shaft; the other — the idler gear — is driven by intermeshing with the first. External gear pumps are known for high pressure capability (up to 210 bar in precision designs), compact and economical construction, accurate flow control at variable speeds, and suitability for low-to-medium viscosity fluids like hydraulic oil, fuel, and chemicals.
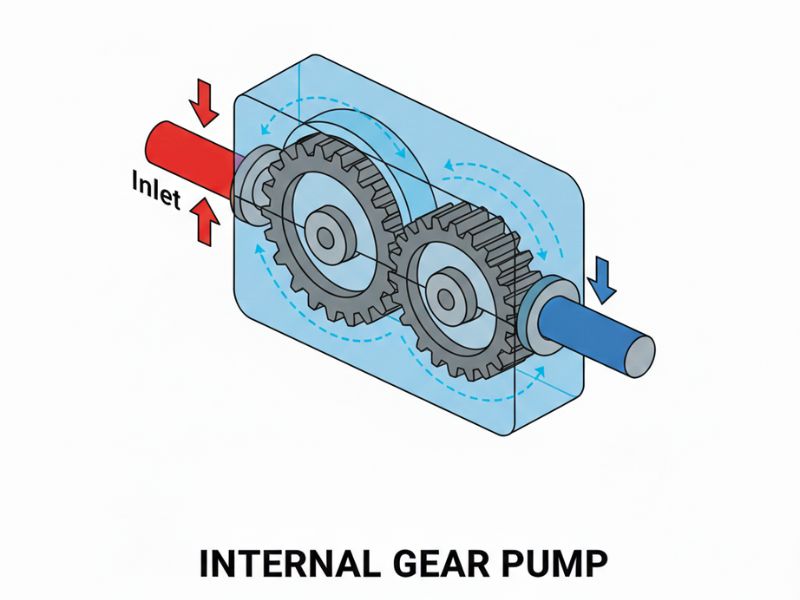
An internal gear pump uses a smaller external gear rotating inside a larger internal (ring) gear, with a crescent-shaped seal separating the suction and discharge zones. Internal gear pumps are preferred for handling very high-viscosity fluids such as bitumen, polymers, resins, and adhesives; for shear-sensitive fluids that must not be damaged during transfer; for bi-directional flow requirements; and for quieter, smoother operation with reduced pulsation.
Advantages: Higher pressure handling, compact and economical construction, accurate flow control, suitable for low-to-medium viscosity fluids.
Disadvantages: Lower tolerance for solids, higher wear under abrasive conditions, limited performance with very high-viscosity fluids.
Advantages: Excellent suction capability, handles very high viscosity fluids, lower shear and quieter operation, better temperature tolerance, can operate bi-directionally.
Disadvantages: Bulkier design, higher initial cost, lower efficiency with thin or low-viscosity fluids.
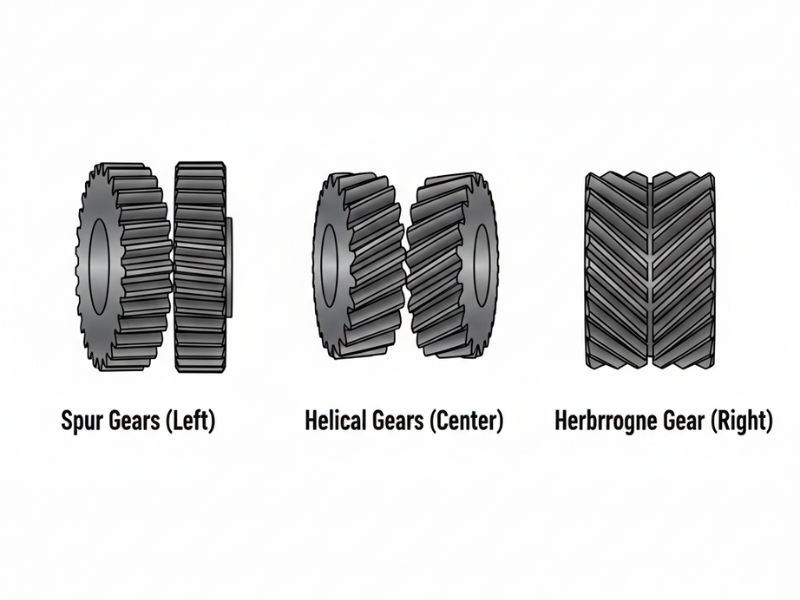

Gear pumps use different gear profiles depending on performance requirements. Spur gears are simple, cost-effective, and widely used. Helical gears provide quieter operation and reduced pulsation. Herringbone gears offer high load capacity and smoother flow. The choice of gear type directly affects noise levels, efficiency, and service life.
Gear pumps are used across a wide range of industries wherever precise, consistent, and pressure-stable fluid transfer is required. The most common applications include:
In industrial environments, gear pumps are preferred when flow must remain stable regardless of pressure changes, fluids are thick or shear-sensitive, accurate volume delivery is required for batching or blending, and equipment must operate continuously with minimal pulsation.
When specifying or evaluating a gear pump, the following parameters matter most:
Understanding how a gear pump compares to other pump types helps clarify when it is the right choice:
Gear pump efficiency increases at optimal RPM, and the pumped fluid itself acts as the internal lubricant — which is why dry running must be avoided. Excessive heat can cause thermal expansion and seizing of tight clearances, so pressure relief valves are mandatory in all gear pump installations. Proper material selection based on fluid chemistry, temperature, and abrasiveness significantly extends service life. Operating within recommended limits ensures stable performance and minimal wear.
Unique Pump Systems is a trusted Indian manufacturer of industrial gear pumps, delivering precision-engineered solutions for demanding applications across manufacturing, chemical, hydraulic, and process industries.
A gear pump is a positive displacement rotary pump that transfers fluid using intermeshing gears to deliver smooth, accurate, and pressure-stable flow. With two main designs — external and internal — gear pumps serve a wide range of industrial applications, especially where viscous fluids, precise dosing, and high reliability are required. Choosing the right gear pump design and manufacturer ensures long service life, operational efficiency, and consistent performance, making gear pumps an essential component in modern industrial fluid handling systems.